Rotation Type: Single-PhaseThis rotation updates a single credential set in place. Old credentials become invalid immediately upon rotation. This means that clients using the previous credentials will fail to authenticate until they retrieve the new credentials.This is a limitation of the SSH provider and cannot be rectified by Infisical.
Prerequisites
- Create an SSH Connection with the Secret Rotation requirements
- Ensure your network security policies allow incoming requests from Infisical to this rotation provider, if network restrictions apply.
Create a Unix/Linux Local Account Rotation in Infisical
- Infisical UI
- API
-
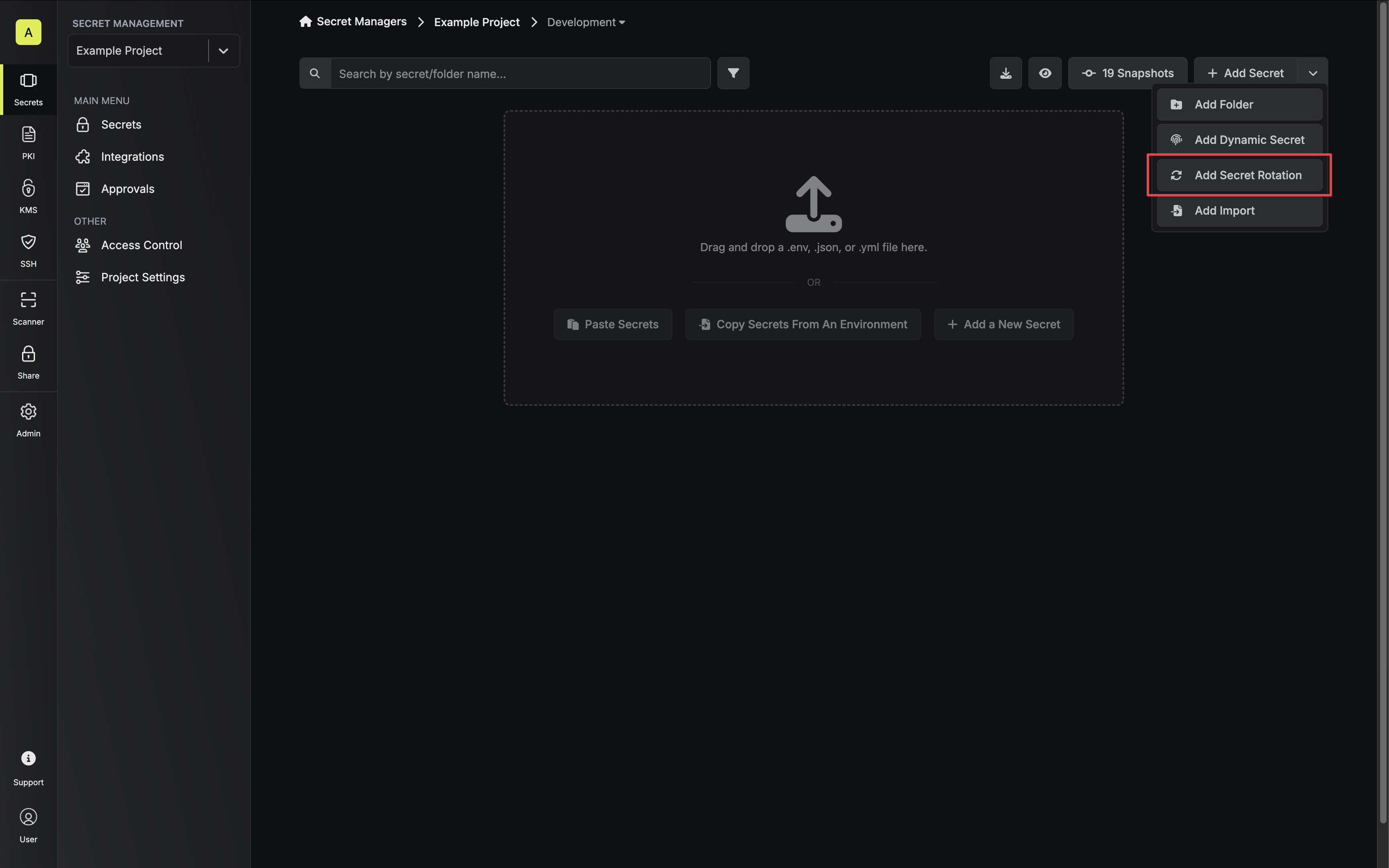
Navigate to your Secret Manager Project’s Dashboard and select Add Secret Rotation from the actions dropdown.
-
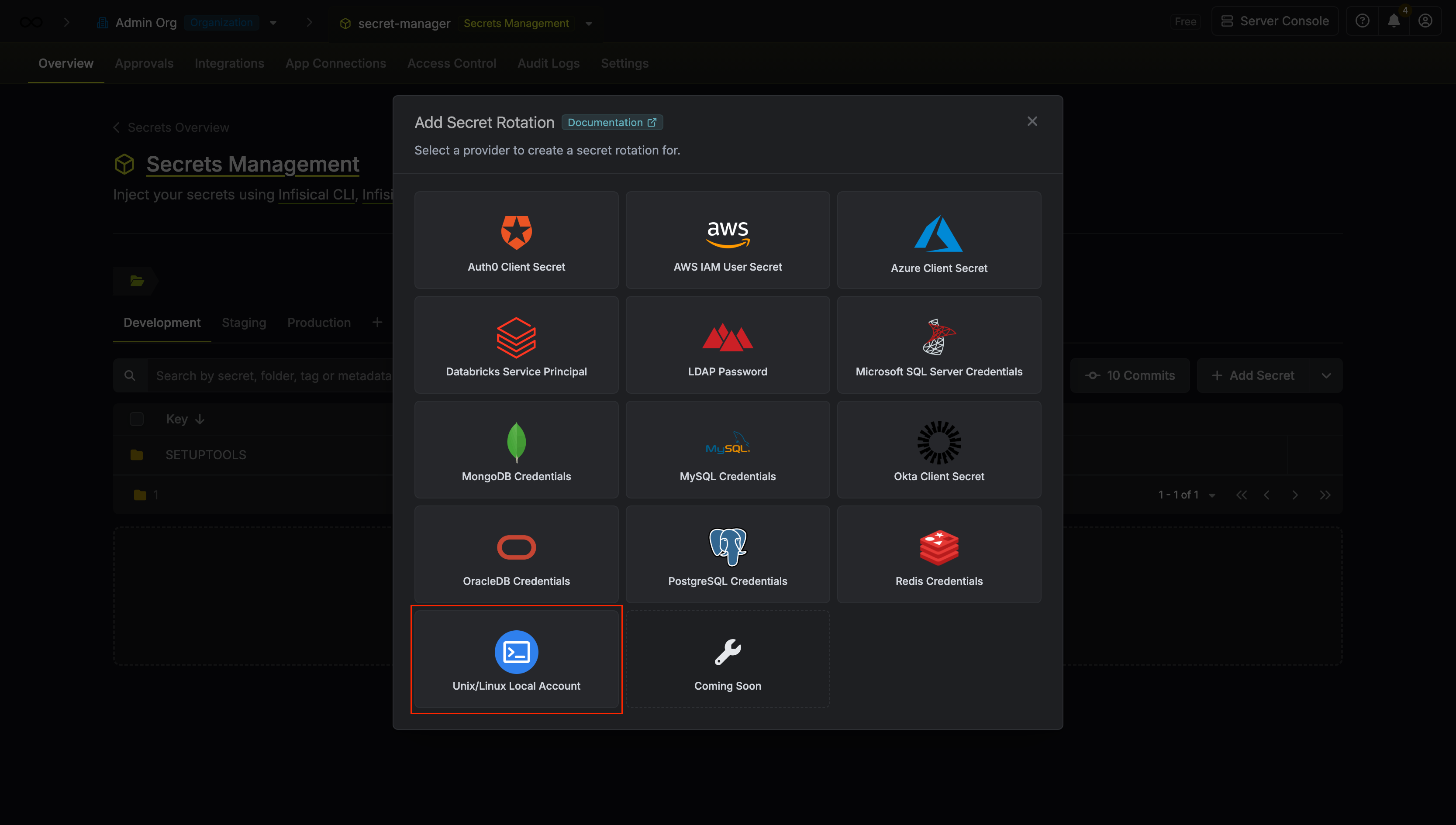
Select the Unix/Linux Local Account option.
-
Select the SSH Connection to use and configure the rotation behavior. Then click Next.
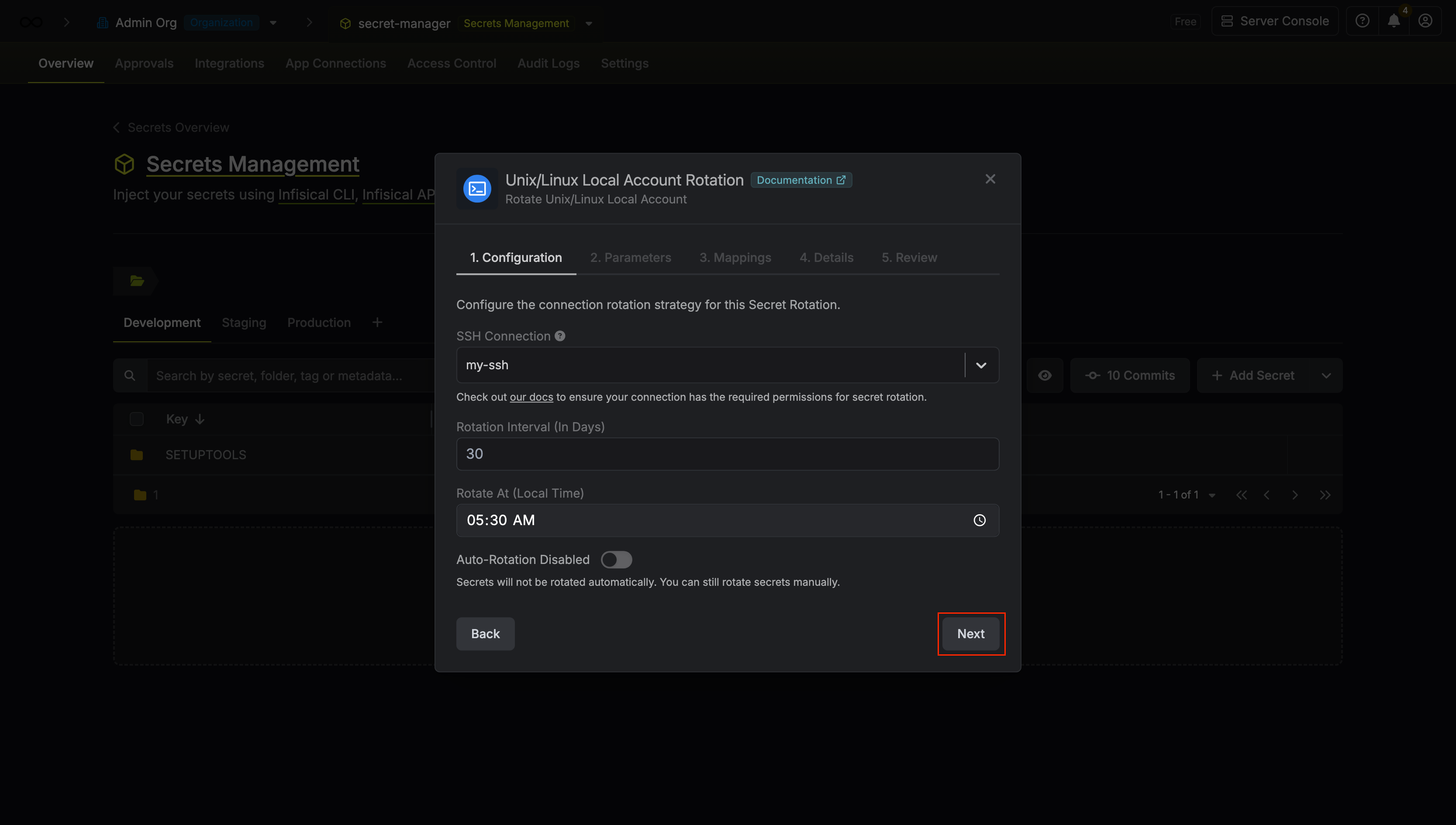
- SSH Connection - the connection that will perform the rotation of the configured user’s password.
- Rotation Interval - the interval, in days, that once elapsed will trigger a rotation.
- Rotate At - the local time of day when rotation should occur once the interval has elapsed.
- Auto-Rotation Enabled - whether secrets should automatically be rotated once the rotation interval has elapsed. Disable this option to manually rotate secrets or pause secret rotation.
Due to Unix/Linux Local Account Rotations rotating a single credential set, auto-rotation may result in service interruptions. If you need to ensure service continuity, we recommend disabling this option. -
Configure the required Parameters for your rotation. Then click Next.
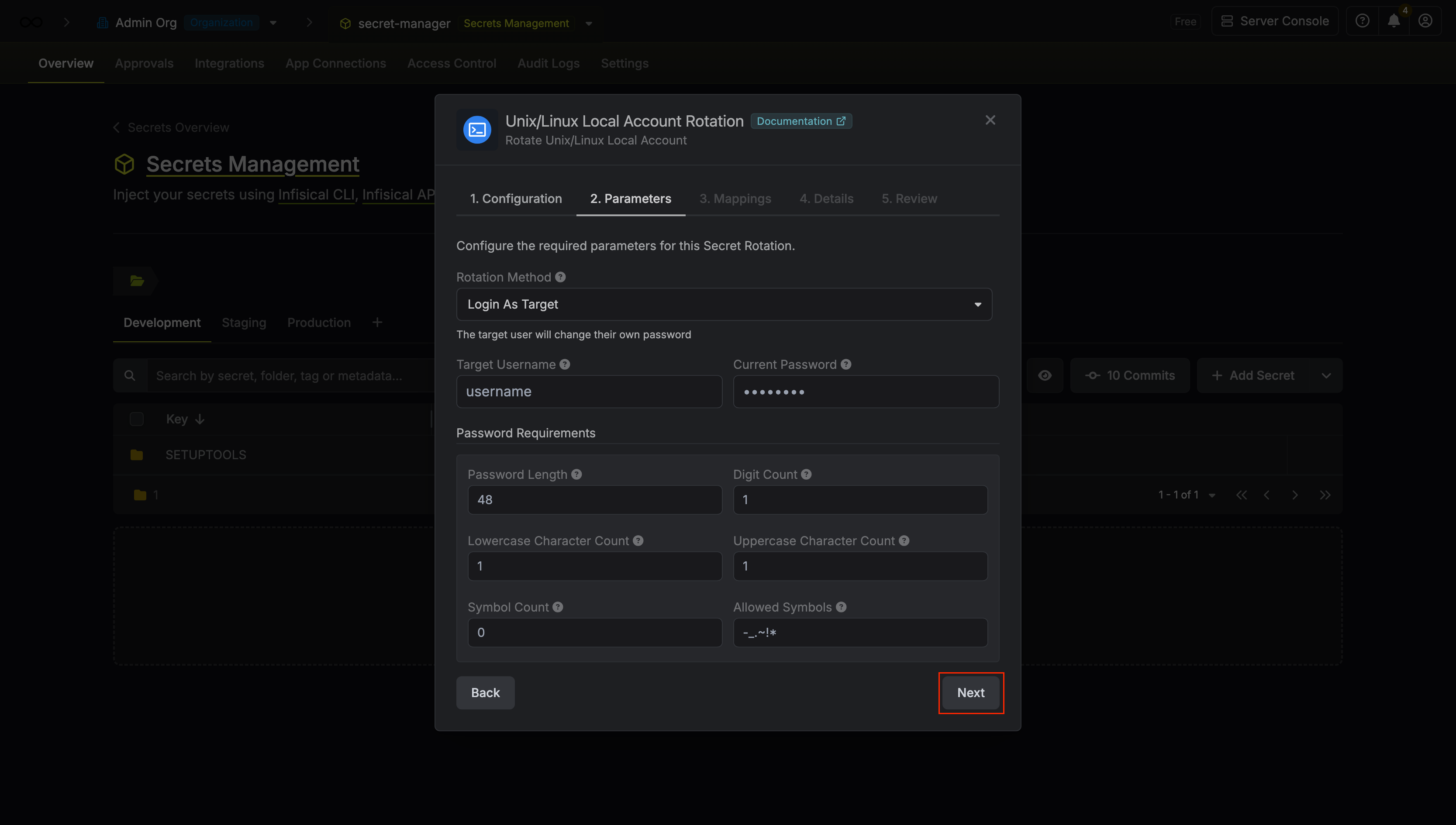
- Rotation Method - The method to use when rotating the target user’s password.
- Login as Target - Infisical will use the provided SSH username and password to log in and rotate its own password.
- Login as Root - Infisical will use the SSH Connection’s credentials to log in and rotate the provided user’s password.
- Username - The target SSH username whose password will be rotated.
- Use Sudo - If true, uses sudo when executing the password rotation command. Defaults to false.
- Current Password - The current password of the target user (required when Rotation Method is set to Login as Target).
- Password Requirements - The constraints to apply when generating new passwords.
-
Specify the secret names that the Unix/Linux credentials should be mapped to. Then click Next.
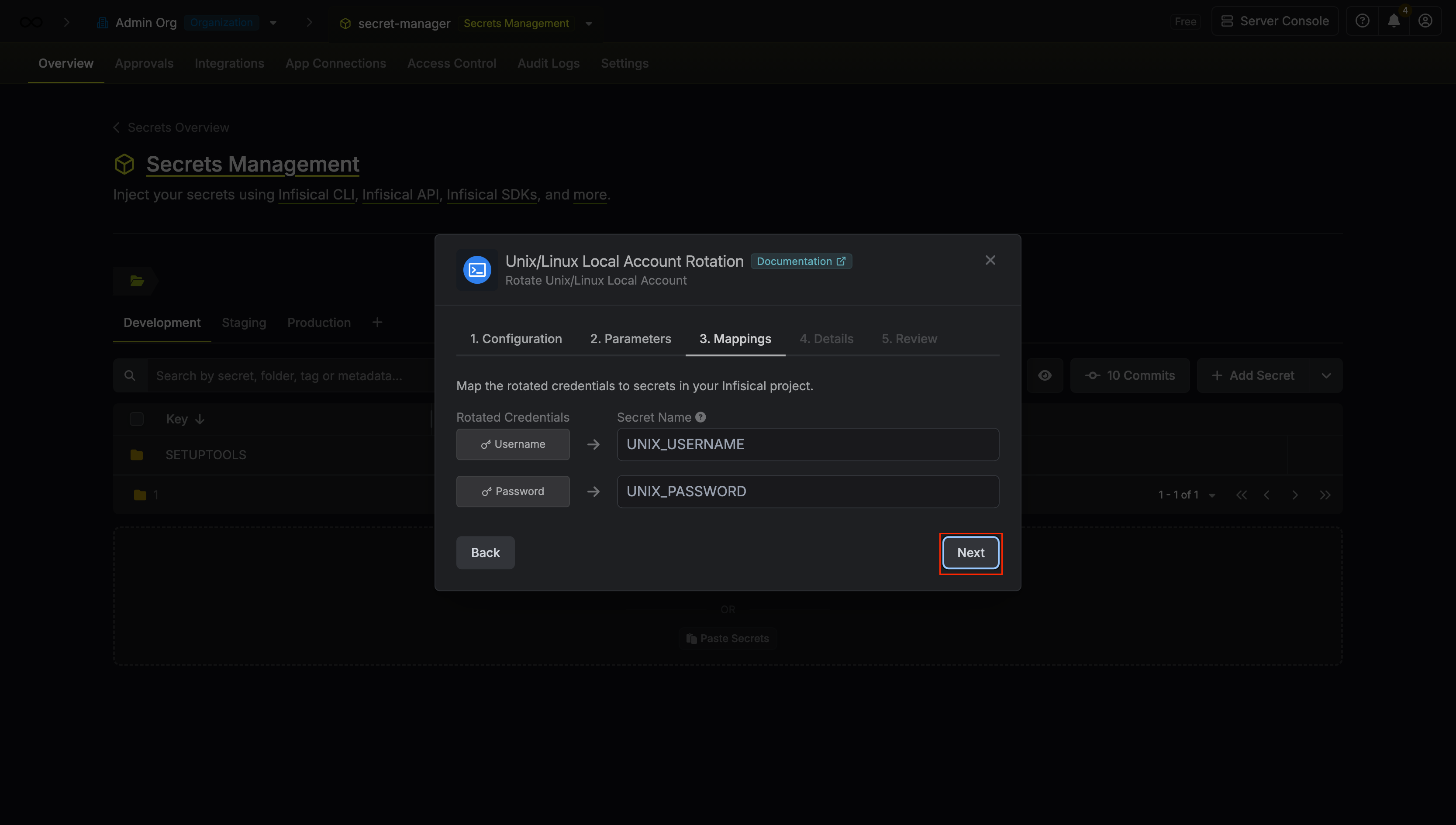
- Username - the name of the secret that the Unix/Linux username will be stored in.
- Password - the name of the secret that the rotated password will be stored in.
-
Give your rotation a name and description (optional). Then click Next.
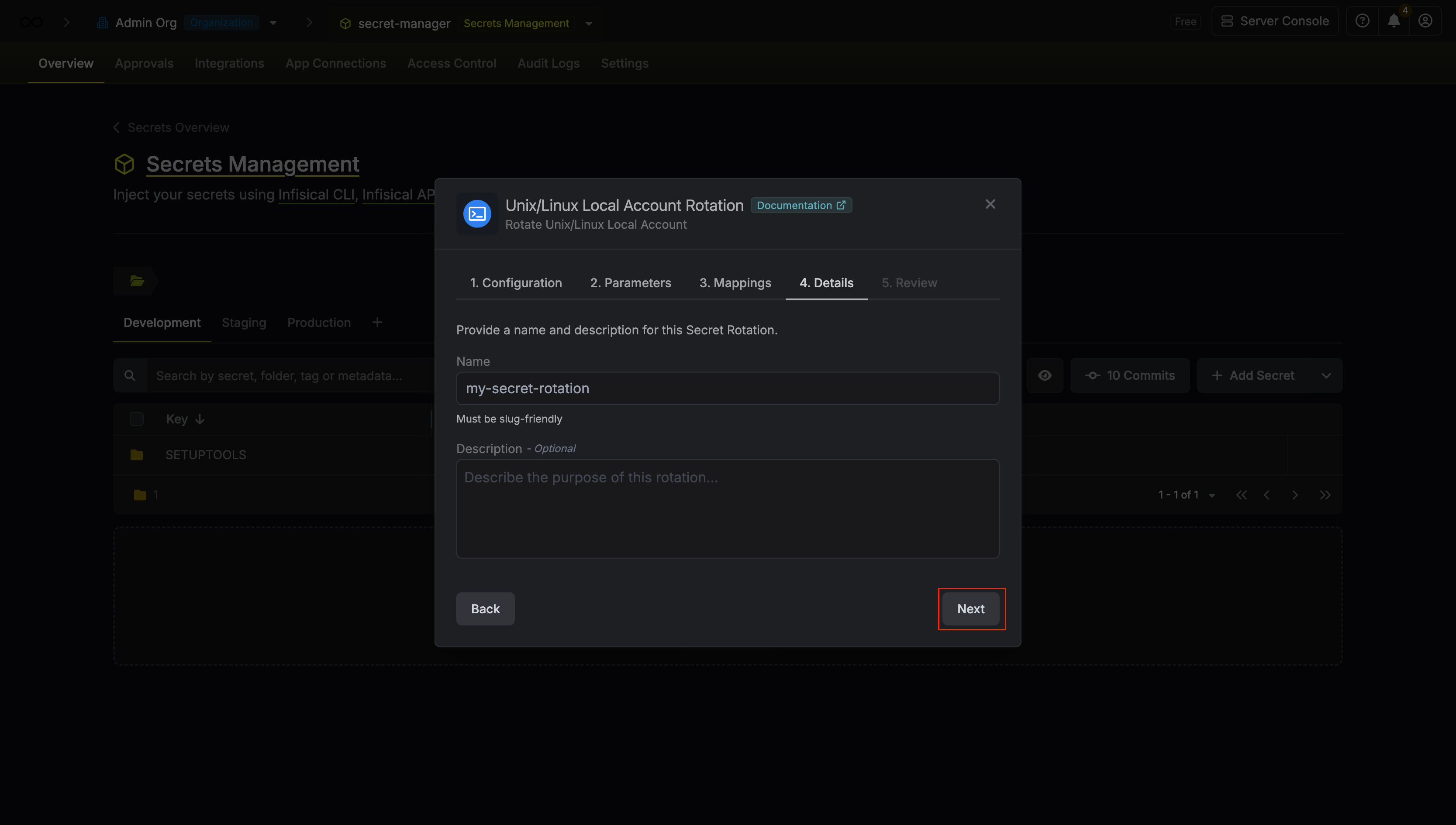
- Name - the name of the secret rotation configuration. Must be slug-friendly.
- Description (optional) - a description of this rotation configuration.
-
Review your configuration, then click Create Secret Rotation.
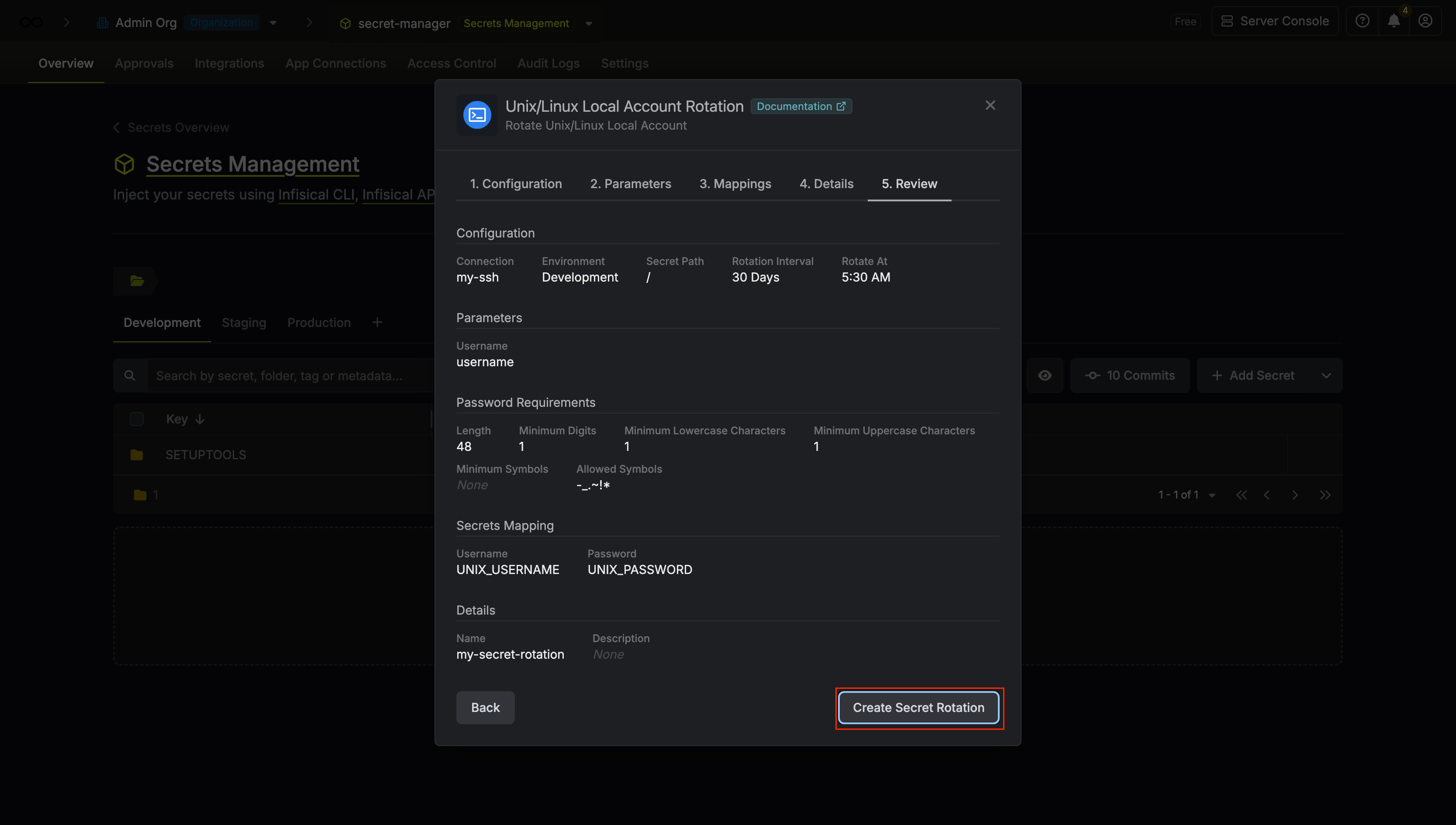
-
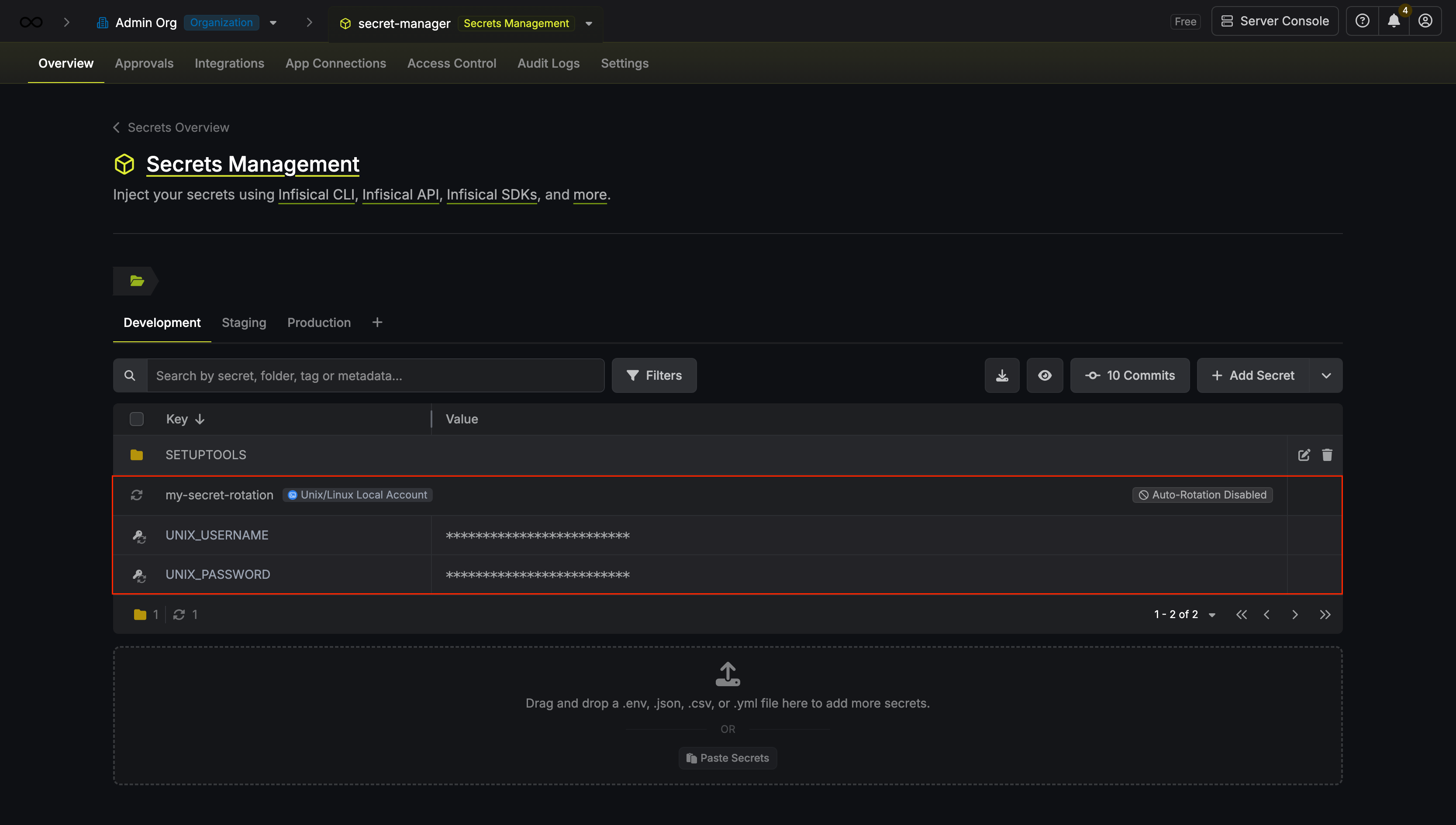
Your Unix/Linux Local Account credentials are now available for use via the mapped secrets.
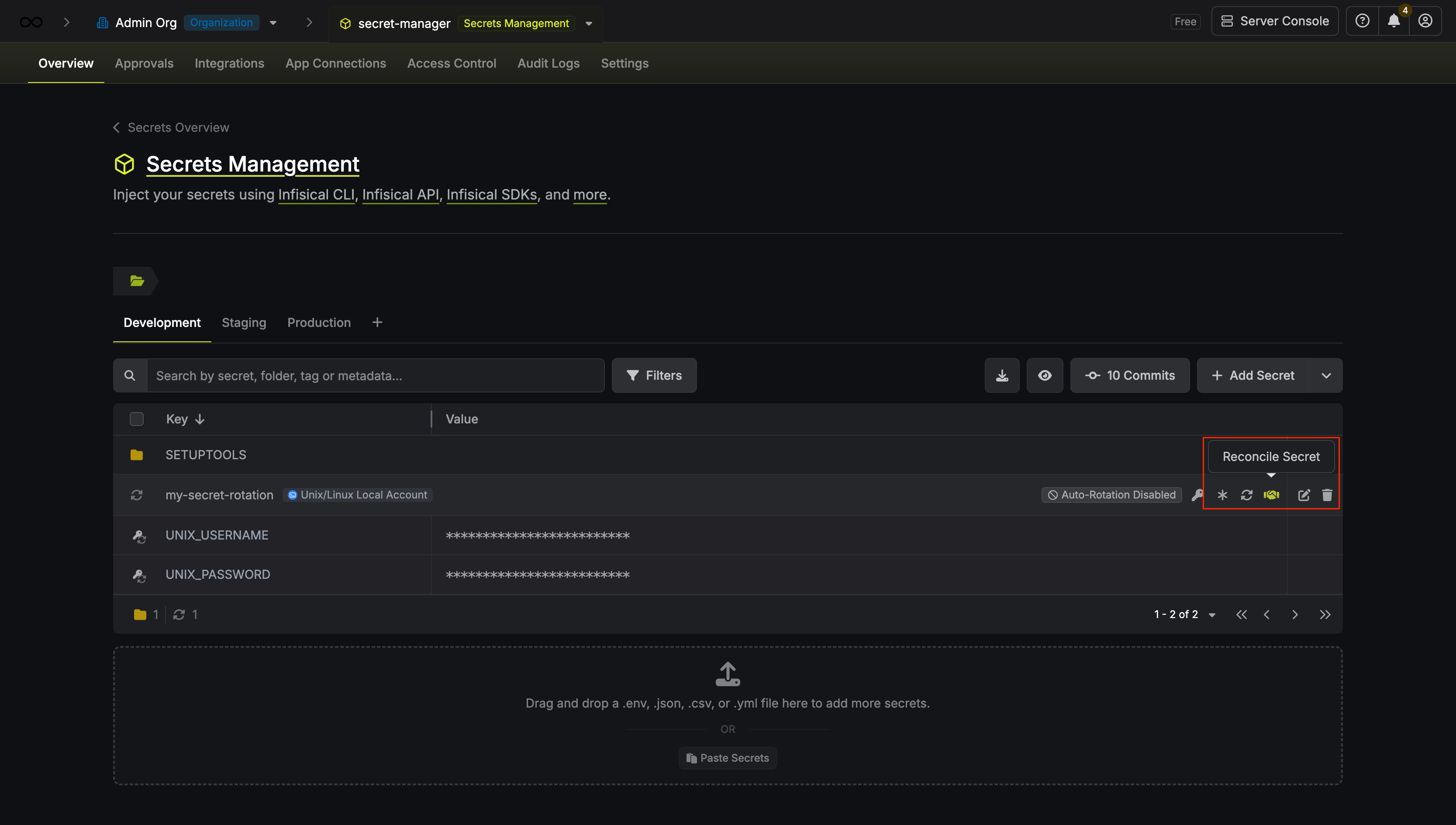
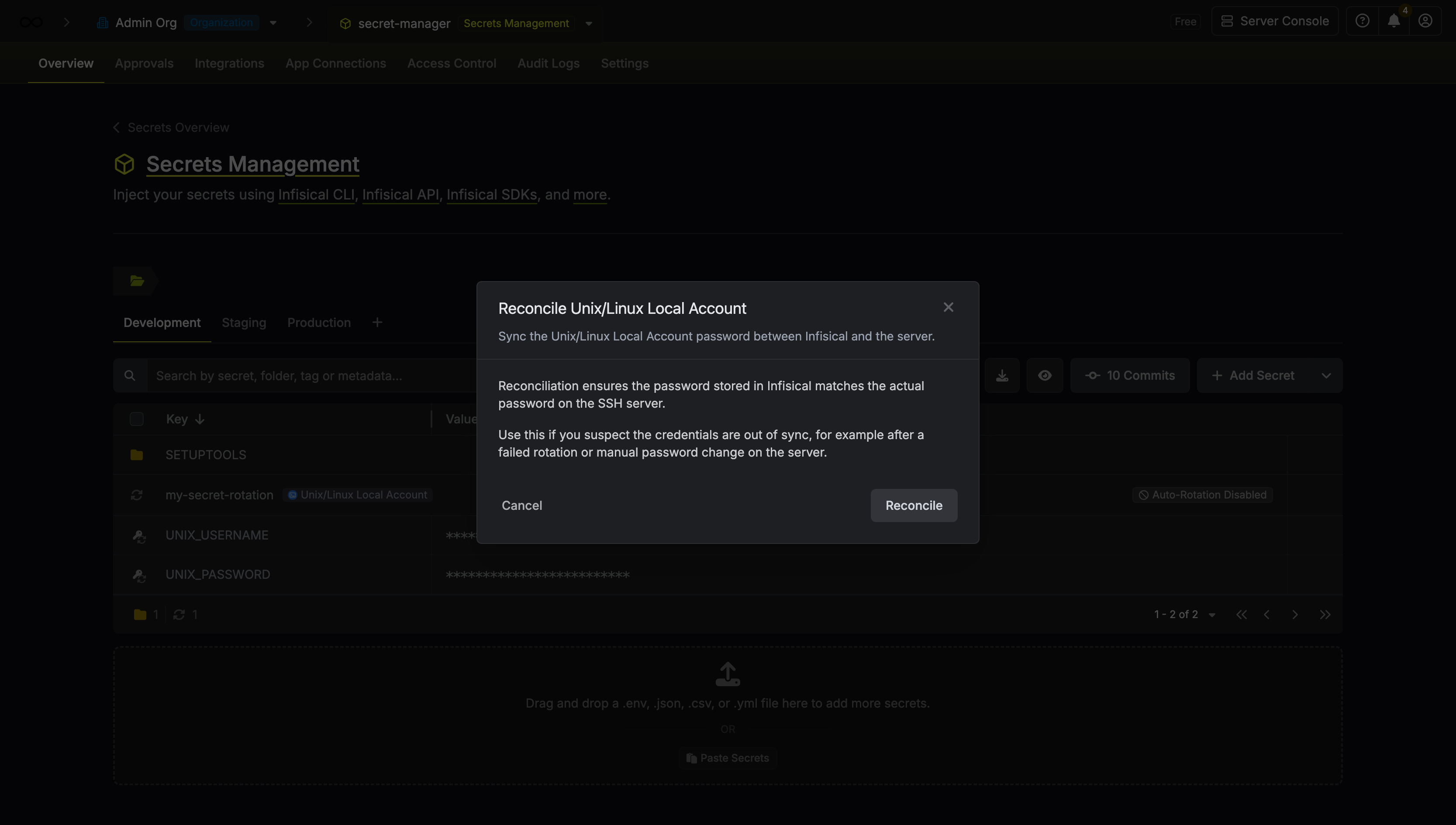
Reconcile Unix/Linux Local Account
If you suspect the credentials are out of sync (for example, after a manual password change on the server), you can regain access by using Reconcile. This will use the configured SSH App Connection’s root account to reset the target user’s password and sync it with Infisical.