- Install the Infisical Operator on your Kubernetes cluster.
- Configure Authentication using Kubernetes Service Accounts.
- Use Each of the three CRDs.
- InfisicalSecret [Sync secrets from Infisical to Kubernetes]
- InfisicalPushSecret [Sync secrets from Kubernetes to Infisical]
- InfisicalDynamicSecret [Manage Dynamic Secrets and automatically create time-bound leases]
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure your environment is ready- Installed tools
- Kubernetes Cluster
- Ensure you have access to a running cluster and connect with kubectl
- PostgreSQL Cluster (for InfisicalDynamicSecret)
- Ensure you have a running database that you have access to
- Clone infisical-guides-source-code repository
- Access to an Infisical instance (cloud or self-hosted)
Step-By-Step Guide
Install the Infisical Operator
The Infisical Operator runs inside your cluster and is responsible for handling secret synchronization events.Verify the operator pod is running:
Create a Machine Identity and Set Up a Project
The operator uses a Machine Identity to authenticate with Infisical through the Kubernetes Auth Method
- Login to Infisical
- Select Organization Access from the left navigational pane
- Create an Identity and give it a name and a role
- Once the Machine Identity is created, copy the Identity ID (will be used later)
- Select the created Machine Identity, and add a Kubernetes Authentication Method. Use these configurations:
- Allowed Service Account Names: infisical-service-account, default
- Allowed Namespaces: default
- Kubernetes Host URL can be found by running
kubectl cluster-info - Token Reviewer JWT / CA Certificate: We will be generating these two later and adding them in later, leave it blank for now
- Once the Machine Identity has been created, navigate back to Overview
- Now select Add New Project
- Add a Project Name, and select Secrets Management as the product type
- Add a description (Optional).
- Once the Project is created, navigate into the Project to Add Secrets. You can add any key-value pair for this example, however if you want to use the InfisicalSecret CRD example provided in this demo, use the following configurations:
- Key: SMTP_HOST
- Value: smtp@gmail.com
- Tags: N/A (Not needed for this demonstration)
- Environments: Production
- Now lets navigate to the Project Access tab on the left hand navigation pane.
- Add the machine identity we created, and give it Admin permissions (just for demonstration purposes)
Set Up RBAC, Service Accounts, and Create Tokens
Now we will be interacting with the local repository you cloned earlier. Make sure you are in the directory that contains the yaml configurations. Assuming you are in your root user directory:
- Create the
infisical-token-reviewerservice account. This Manifest creates a service account that the Infisical Operator uses to authenticate with Kubernetes for token reviews. It allows Infisical to validate Kubernetes tokens securely during the Machine Identity authentication process.
- Create the token for the reviewer service account. This Yaml defines a service account token secret linked to the reviewer account created above. It generates a JWT token that Infisical uses for the Kubernetes Auth Method in your Machine Identity configuration.
- This file binds the
infisical-token-reviewerservice account to the built-insystem:auth-delegatorClusterRole. That role allows the service account to perform token review and authentication delegation requests on behalf of other service accounts - a key part of Kubernetes-based identity verification. Without this binding, the Infisical Operator wouldn’t have permission to validate tokens.
- Create the service account that will be used by the InfisicalSecret. This file creates a dedicated service account
infisical-service-accountthat the Infisical Operator uses to access and sync secrets within your cluster. It operates as the Operator’s working identity in your cluster, separate from the token reviewer.
- Create the token for the Infisical service account. This manifest defines a token secret for the
infisical-service-account. It allows the Infisical operator to authenticate against Infisical’s API when syncing secrets. The token will then be manually patched and associated with the service account to make sure Kubernetes mains it persistently.
- Apply the patch to manually associate the token secret
- Create the JWT Token and Certificate and add it to the Machine Identity we created under Kubernetes Auth. For the generated CA, navigate to the Advanced tab to paste the certificate:
- JWT Command
- CA Command
Verify Service Accounts and Tokens
- Check to see if the service accounts were created
- Verify the tokens were created and linked
Create the InfisicalSecret CRD
The InfisicalSecret CRD tells the operator to sync secrets from Infisical to Kubernetes. By referencing your
identityID, projectSlug, and envSlug, this CRD tells the Infisical Operator which Infisical secrets to fetch and how to format them into a Kubernetes Secret. Make sure to edit the provided CRD to match your specific Machine Identity ID, Project ID, and which environment your secrets are being pulled from (default is prod).- Project Slug: Can be found when you select your project and navigate to settings
- Identity ID: Can be found when you select your machine identity from your organization’s access control
- After editing the
example-infisical-secret-crd.yamlto contain your demo-specific values, apply the yaml in your cluster
Verify the InfisicalSecret Status
- Check that the
InfisicalSecretwas created successfully
- Check that the operator created the
managed-secret
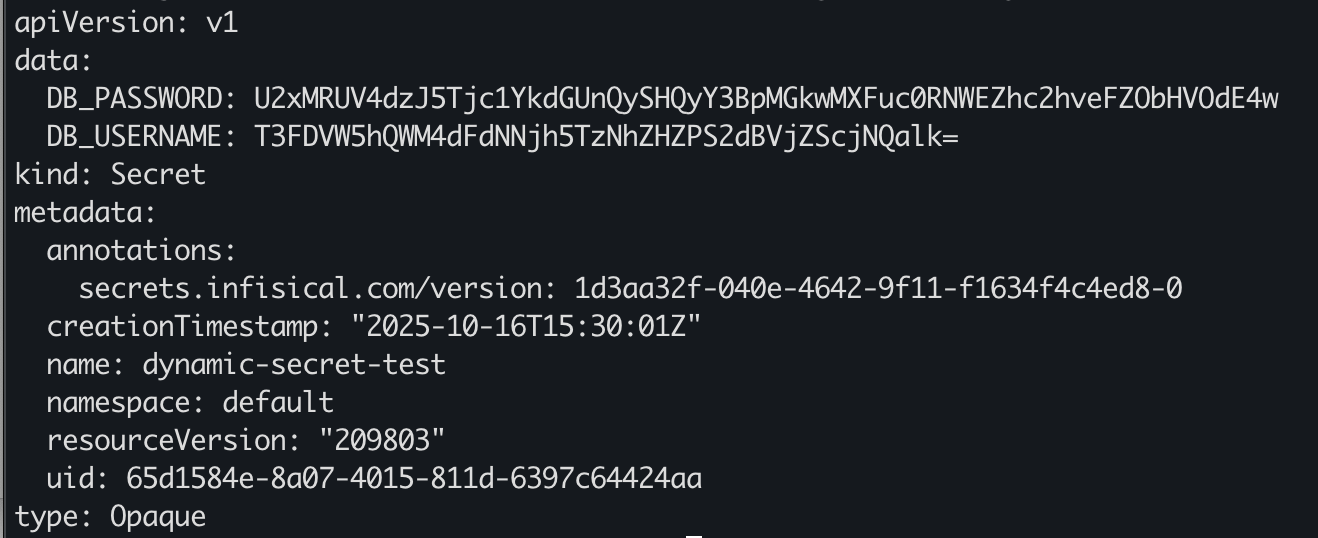
- View the secret contents (base64 encoded)
Deploy the Demo Application
- Deploy the nginx demo deployment that will use the managed secret.
- Wait 15-20 seconds and then verify the deployments
Verify the Secret is Injected Into the Pod
- Check that the environment variable is in the running pod. If everything was successful, at this point you should be able to see the secret populate in the kubernetes pod and have a successful sync from Infisical to Kubernetes.
Create a Kubernetes Secret to Push Up to Infisical
Now that we have successfully synced secrets from Infisical to Kubernetes, lets explore how we can push Kubernetes Secrets to Infisical.
- Either create a Kubernetes Secret via yaml, or use the one in the repository.
- Verify creation of the secret
Create the InfisicalPushSecret CRD
The InfisicalPushSecret CRD tells the operator to sync secrets from Kubernetes to Infisical. Make sure you edit the CRD to include the specific Project Slug, and Identity ID. The other values present in
example-push-secret.yaml should be configured based on the previously committed yaml configurations.- Apply the InfisicalPushSecret CRD provided after making the necessary changes
-
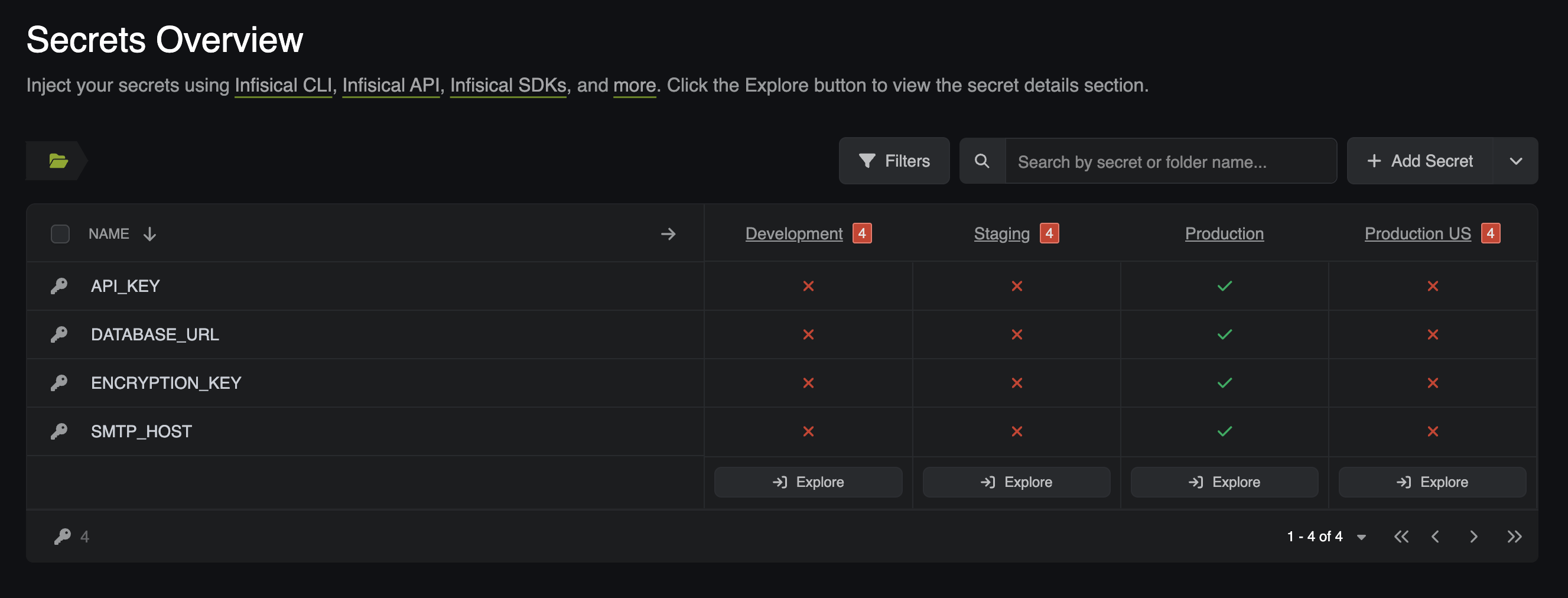
Once your CRD has been configured, go back to your project within Infisical and check to see if your secrets have populated there.
Create the InfisicalDynamicSecret CRD
The InfisicalDynamicSecret CRD allows you to sync dynamic secrets and create leases automatically in Kubernetes as native Kubernetes Secret resources Any Pod, Deployment, or other Kubernetes resource can make use of dynamic secrets from Infisical just like any other Kubernetes secret.
-
Navigate to your Infisical Project and click on the dropdown next to Add Secret. From here you will select Add Dynamic Secret
- Select SQL Database as the service you would like to connect to.
- Select PostegreSQL as the database service. Enter in the connection details for your database, specifically the Host, Port, User, Password, and Database Name.
- For the Secret Name, if you want to use the same name as the one in the cloned InfisicalDynamicSecret CRD, use the name dynamic-secret-lease. Otherwise you will need to change the dynamicSecret.secretName config in the InfisicalDynamicSecret CRD to whatever you name the secret here.
- In the CA (SSL) section, make sure to upload the CA Certificate for your database.
- Finally, select Prod as the environment (we are keeping this configuration as part of the demonstration).
-
Edit the
dynamic-secret-crdwith the proper machine Identity ID, Project Slug, dynamicSecret.secretName (same as the Secret Name you gave to the dynamic secret in Infisical), and managedSecretReference.secretName (name of the kubernetes secret that Infisical Operator will create/populate in the cluster).- If you want to keep the managedSecretReference.secretName then you can leave it as dynamic-secret-test
- Once the changes have been saved, apply the yaml:
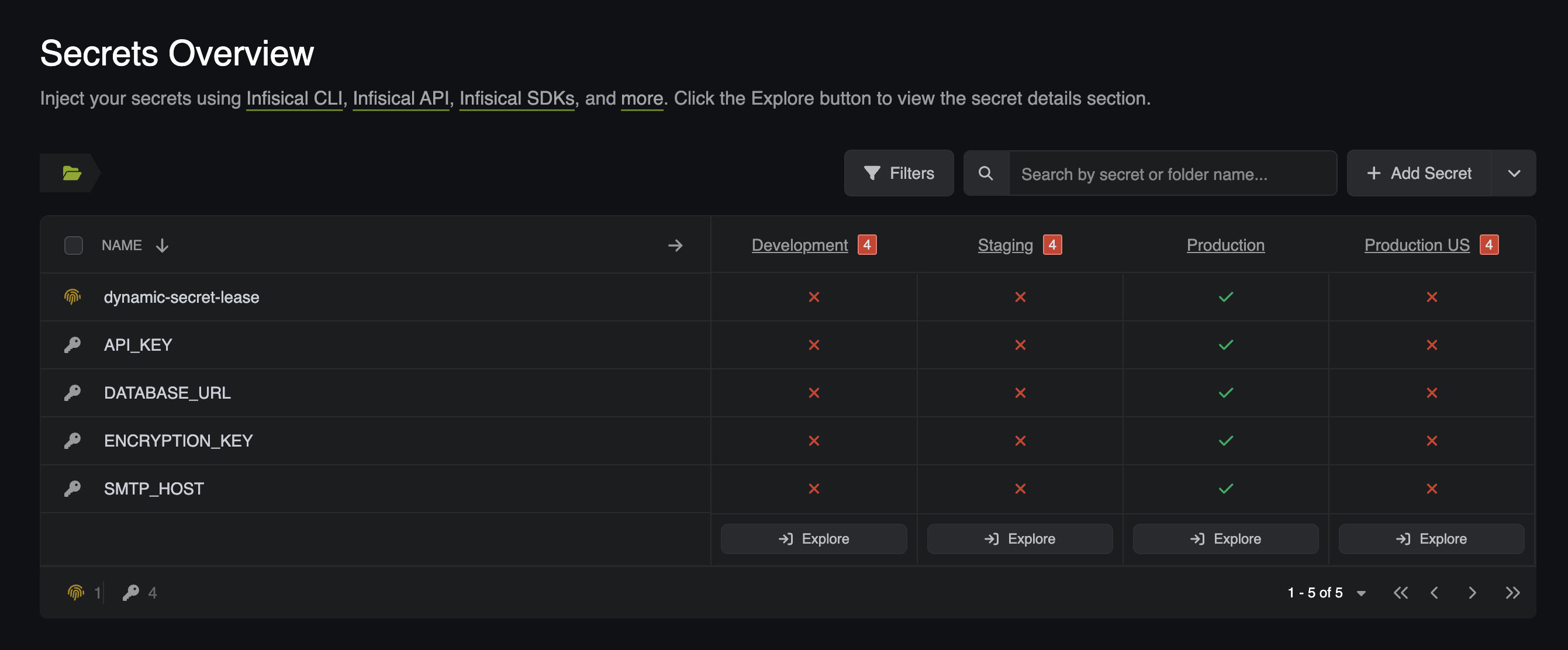
- After applying the CRD, you should notice that the dynamic secret lease has been created and synced with your cluster. Verify by running:
-
Once the dynamic secret lease has been created, you should see that the secret has data that contains the lease credentials.