Concept
MCP Servers are external services that expose tools and capabilities through the Model Context Protocol. By connecting MCP servers to Infisical, you can centrally manage access to tools like Notion, GitHub, Slack, and more. When you add an MCP server to Infisical, the platform discovers all available tools from that server and allows you to make them accessible through MCP Endpoints.Supported MCP Servers
Infisical supports connecting to any remote MCP server that implements the Model Context Protocol over HTTP with OAuth authentication. Popular MCP servers include:- Notion - Search, create, and manage Notion pages and databases
- GitHub - Manage repositories, issues, pull requests, and more
- Slack - Send messages, manage channels, and interact with workspaces
- Google Drive - Access and manage files and documents
- Linear - Manage issues and projects
Infisical connects to MCP servers over HTTP using the standard remote MCP protocol.
Authentication
MCP servers typically require authentication to access their tools. Infisical supports OAuth authentication, which handles the authorization flow automatically. Some MCP servers support Dynamic Client Registration, which means Infisical can automatically register as an OAuth client. For servers that don’t support this (like GitHub), you’ll need to manually create an OAuth application and provide the client credentials.Credential Modes
When adding an MCP server, you choose how credentials are managed:Shared Credentials
You (the administrator) authorize the MCP server once, and all users who access tools through this server use your credentials.Best for: Shared service accounts, servers without per-user permissions, simplified management.
Personal Credentials
Each user must authenticate with the MCP server individually before using its tools. Their credentials are stored securely by Infisical.Best for: Per-user audit trails, user-specific permissions, compliance requirements.
Guide to Adding an MCP Server
In the following steps, we explore how to add an MCP server to your Agentic Manager project.- Infisical UI
1
Navigate to MCP Servers
Head to your Agentic Manager project and select MCP Servers from the sidebar, then click Add MCP Server.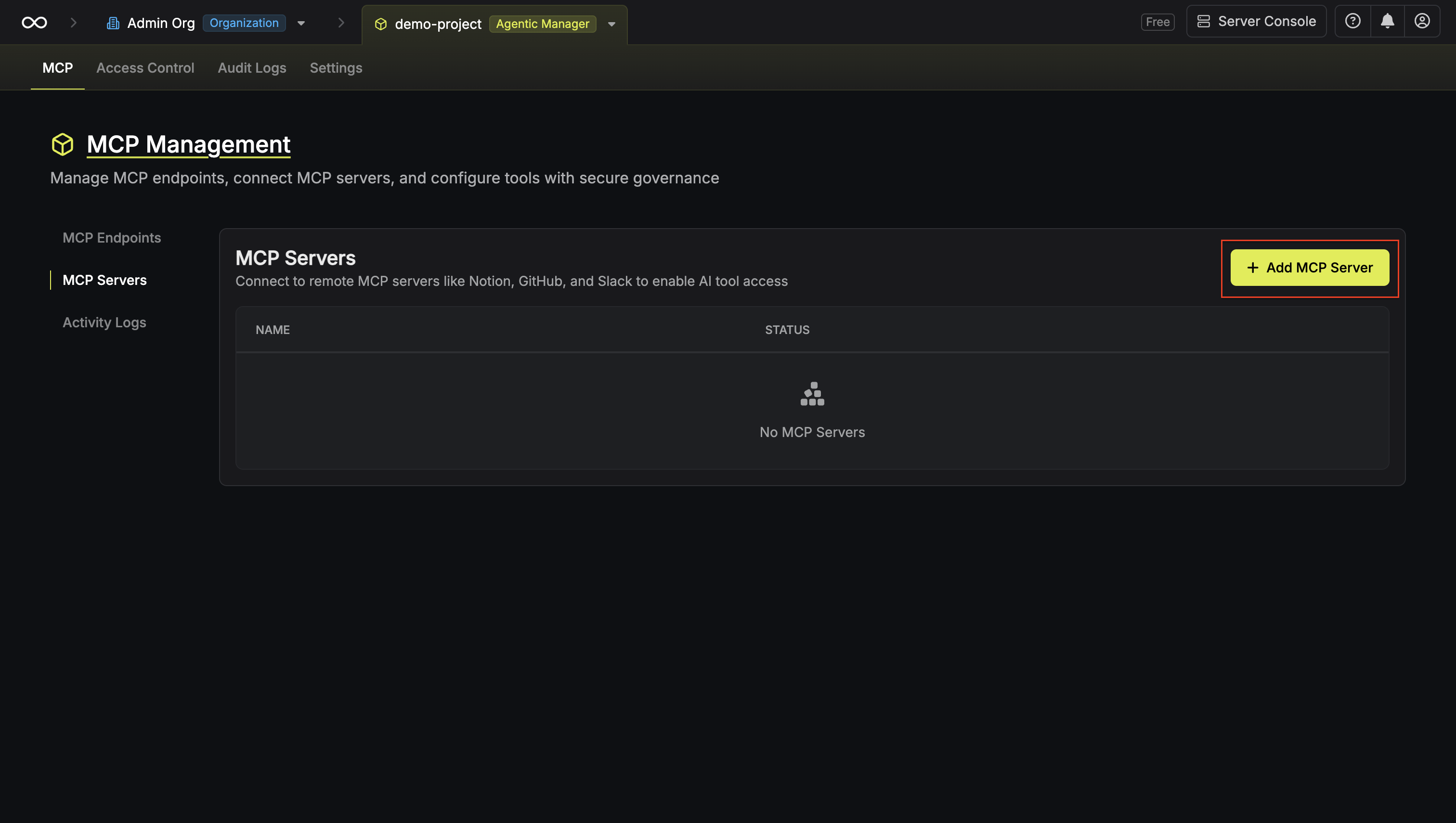

2
Configure server details
Enter the following details for your MCP server:
- Name: A friendly name to identify this server (e.g., “Notion”, “GitHub”)
-
URL: The MCP server endpoint URL (e.g.,
https://mcp.notion.com/mcp) -
Credential Mode: Choose between Shared Credentials or Personal Credentials
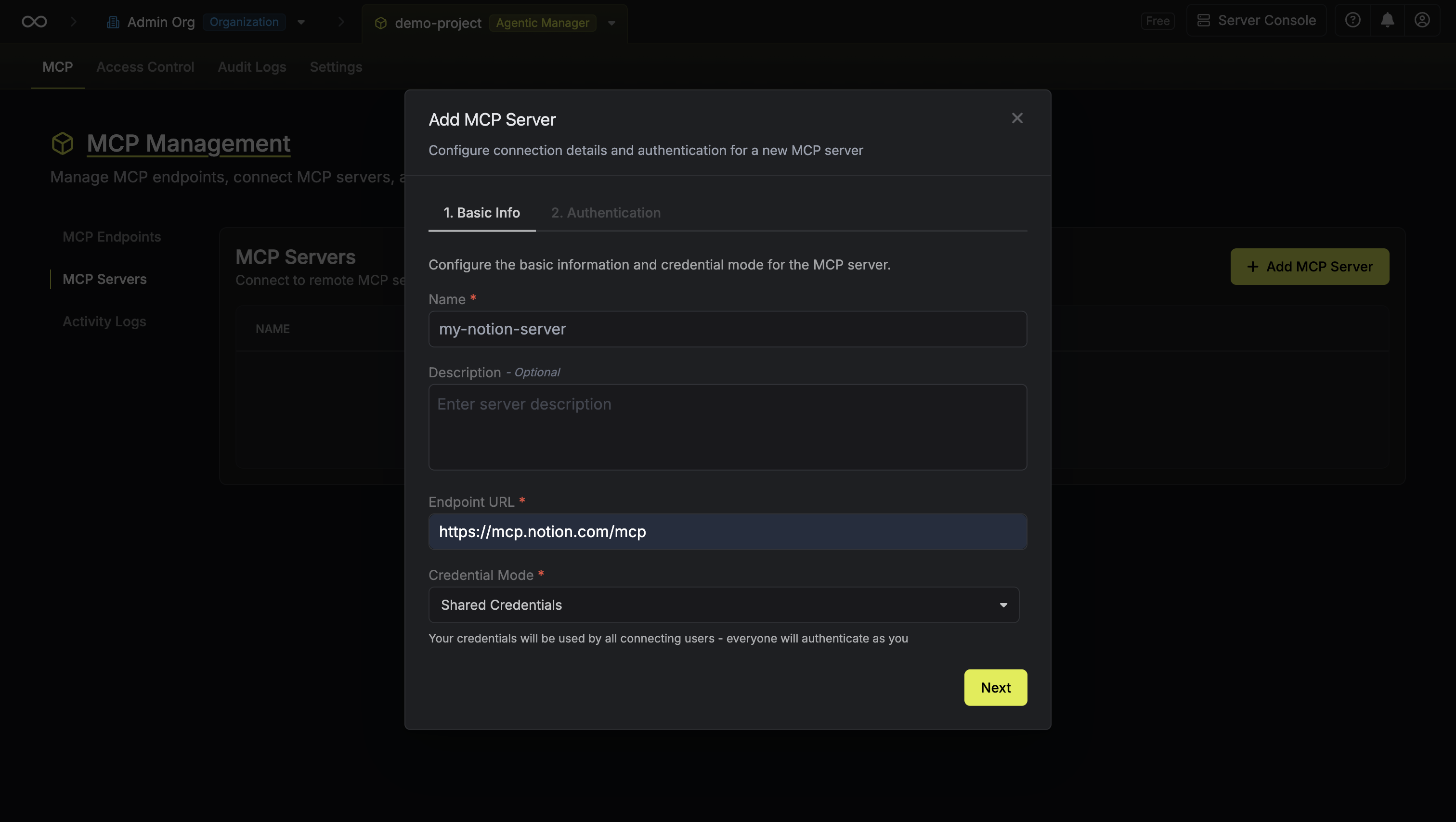
3
Configure authentication
For OAuth authentication, you may need to provide credentials depending on the server:For servers with Dynamic Client Registration (e.g., Notion):
- Simply click Authorize to complete the OAuth flow
- Create an OAuth application in the service’s developer settings
- Enter the Client ID and Client Secret
-
Click Authorize to complete the OAuth flow
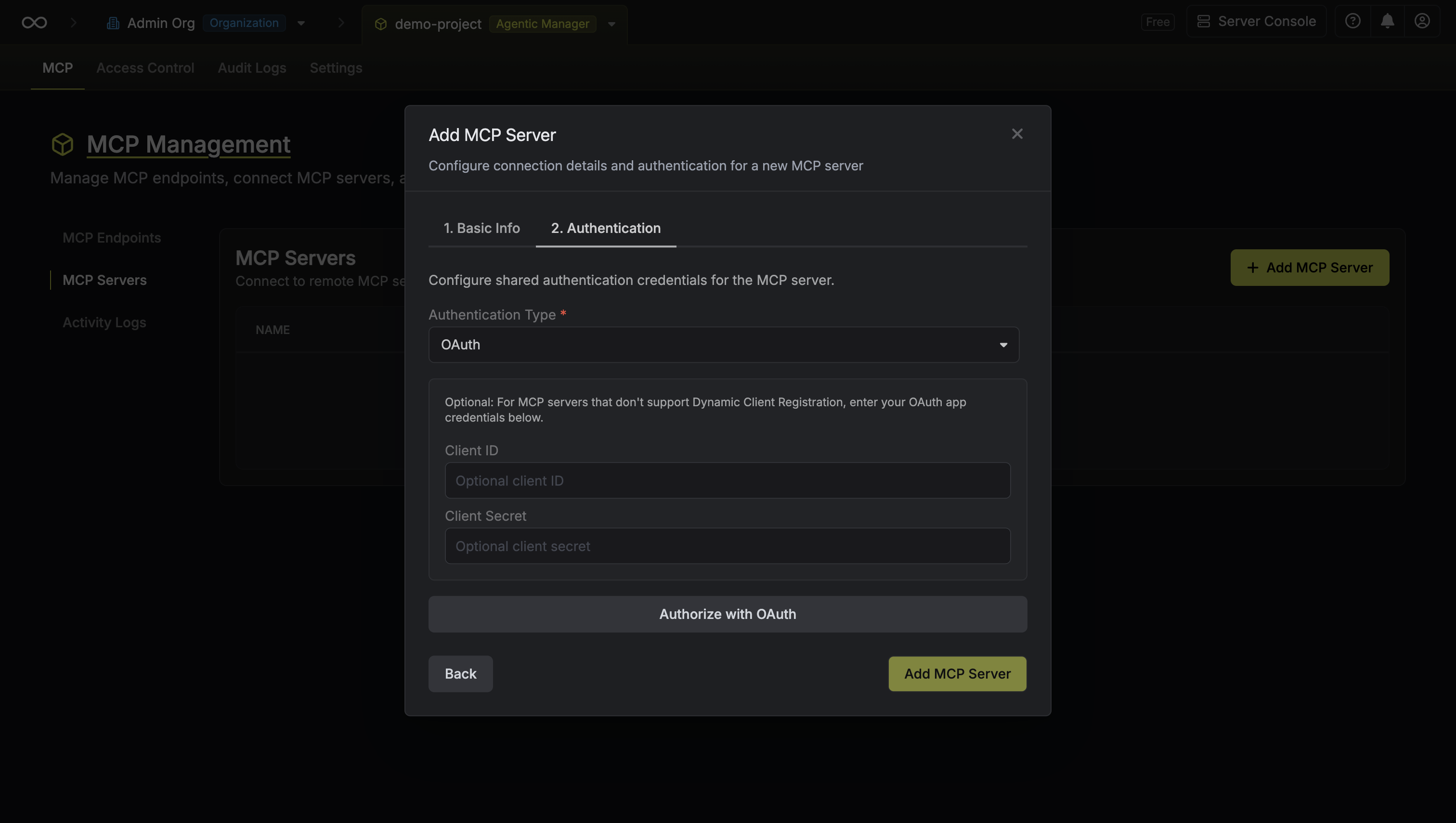
4
Review available tools
After authorization, Infisical discovers and displays all tools available from the MCP server.You can view each tool’s name and description. These tools can now be enabled in MCP Endpoints.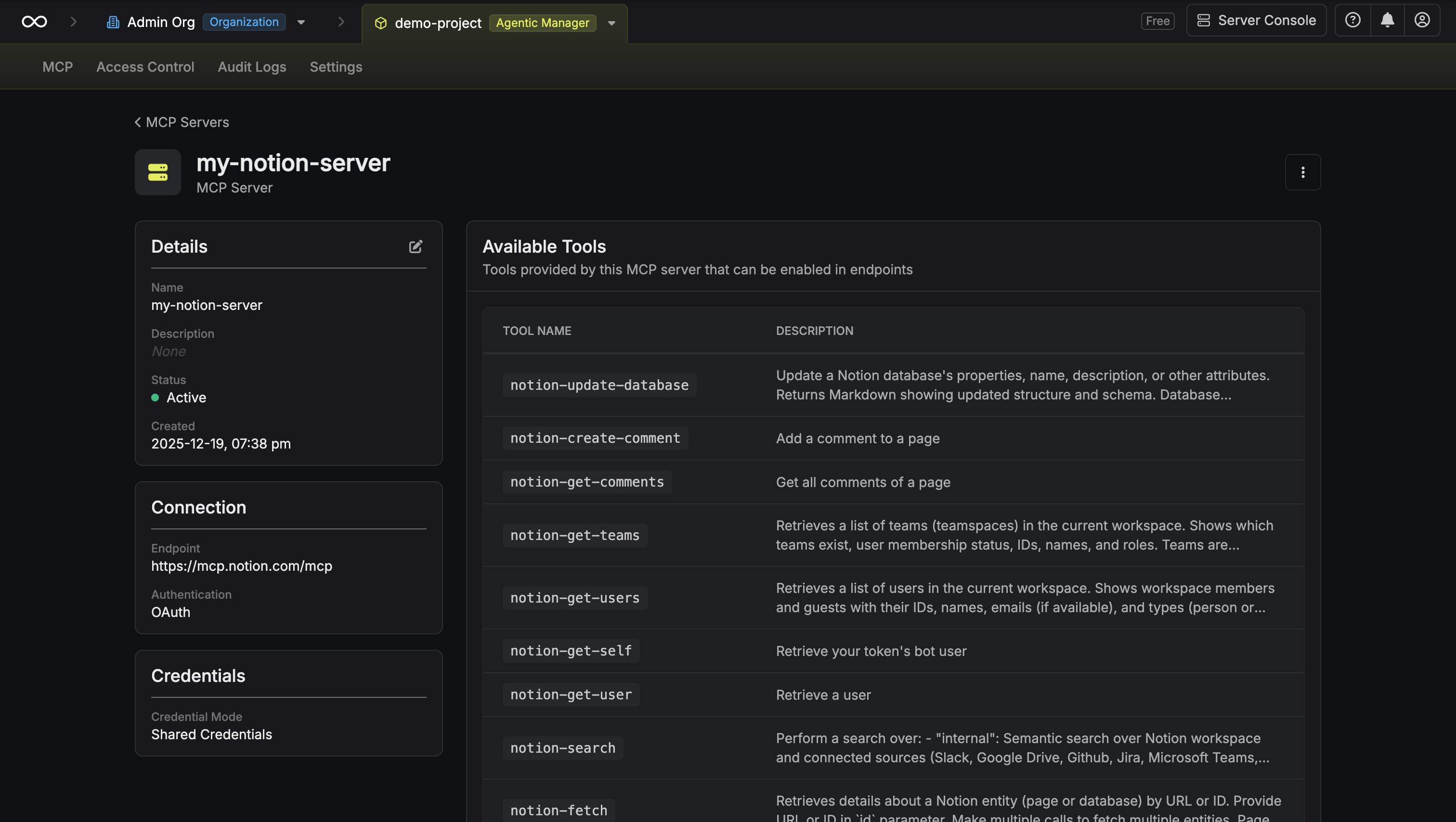

FAQ
What MCP server URLs should I use?
What MCP server URLs should I use?
Each MCP server provider publishes their endpoint URL. Common examples:
- Notion:
https://mcp.notion.com/mcp - GitHub:
https://api.githubcopilot.com/mcp/
How do I create OAuth credentials for GitHub?
How do I create OAuth credentials for GitHub?
- Go to GitHub Settings → Developer settings → OAuth Apps
- Click “New OAuth App”
- Set the Authorization callback URL to your Infisical instance
- Copy the Client ID and generate a Client Secret
- Use these credentials when adding the GitHub MCP server
Can I change the credential mode after adding a server?
Can I change the credential mode after adding a server?
Yes, you can update the credential mode by editing the MCP server configuration. Note that changing from shared to personal credentials will require users to re-authenticate.
What happens if the MCP server goes offline?
What happens if the MCP server goes offline?
If an MCP server becomes unavailable, tool invocations through endpoints connected to that server will fail. The Activity Logs will capture these failures for troubleshooting.

